Description
Components and Functionality:
-
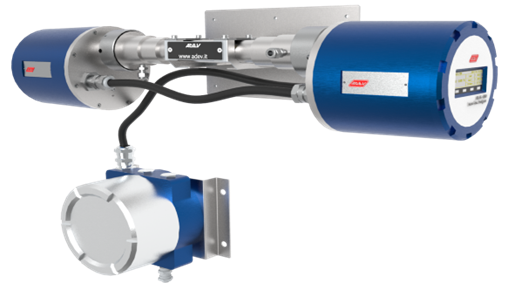
Tunable Diode Laser: The heart of the TDLAS system. This semiconductor laser can be precisely tuned to emit light at specific wavelengths that correspond to the absorption lines of the target gas molecule.
-
Optical System: Directs the laser beam through the gas sample and to a detector. This may involve beam shaping optics, lenses, and mirrors to ensure optimal beam alignment and maximize signal strength.
-
Gas Cell (or Path): The region where the laser beam interacts with the gas sample. The path length can be varied depending on the application and the desired sensitivity.
-
Detector: Typically a photodiode that converts the transmitted light intensity into an electrical signal.
-
Electronics and Data Acquisition: Processes the detector signal, amplifies it, and converts it into a digital format for data analysis.
Key Advantages of TDLAS:
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: TDLAS offers exceptional sensitivity and selectivity for detecting and quantifying specific gases in complex mixtures.
-
Real-Time Analysis: Enables rapid and continuous gas measurements, crucial for process control and monitoring applications.
-
Non-Intrusive Measurements: In many cases, TDLAS can be used for non-invasive measurements, eliminating the need for sample extraction.
-
Compact and Portable: Advances in laser technology and miniaturization have led to the development of compact and portable TDLAS sensors.
-
Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of gases and applications, including environmental monitoring, industrial process control, and medical diagnostics.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.